
adapted from
PLoS supp. material
by Hermann Cuntz

![]()

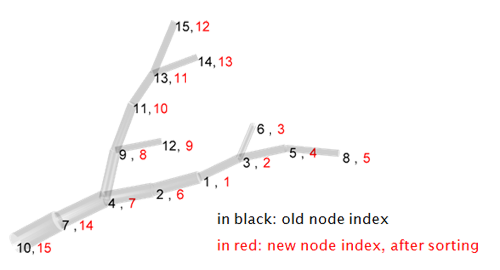
Sorts the labels (indices) of nodes of tree intree to conform to BCT,
an order in which elements are arranged according to their hierarchy keeping
the sub-tree structure intact
(see introduction section
“sorted and equivalent trees”).
Many isomorphic BCT order structures exist, this one is created by switching
the location of each node one at a time to the right neighbour position
of their parent node.
For a unique sorting use '-LO' or ‘-LEX' options.
'-LO' orders the indices using path length and level order. This results in a relatively unique equivalence relation.
'-LEX‘ orders the BCT elements lexicographically. This makes less sense but results in a purely unique equivalence relation.
"sort_tree" affects all vectors of form Nx1 attributed to the tree accordingly..
Example: after redirecting the tree from a different root (see “redirect_tree”) the nodes are scrambled. Try out:
>> rtree = redirect_tree (sample2_tree, 5);
>> sort_tree (rtree, '-s');

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 License